Lanca Canonical Bridge Technical Architecture
Lanca Canonical Bridge implements a canonical bridging architecture that ensures 1:1 backing of bridged assets through a Lock-Release mechanism on L1 and Burn-Mint mechanism on destination chains. The system is designed with security, capital efficiency, and scalability as core principles.
Architecture Diagram
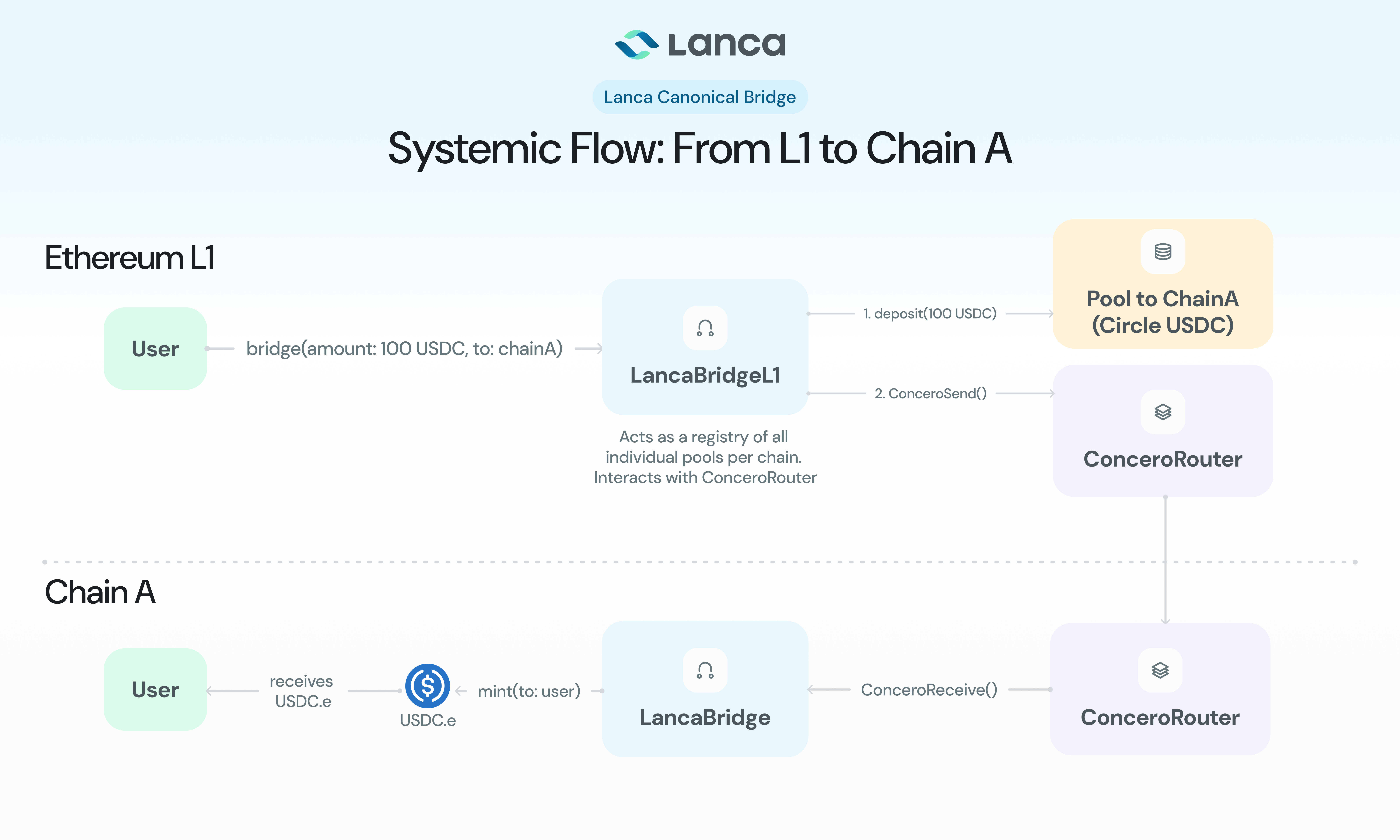
Systemic Flow: From L1 to Chain A
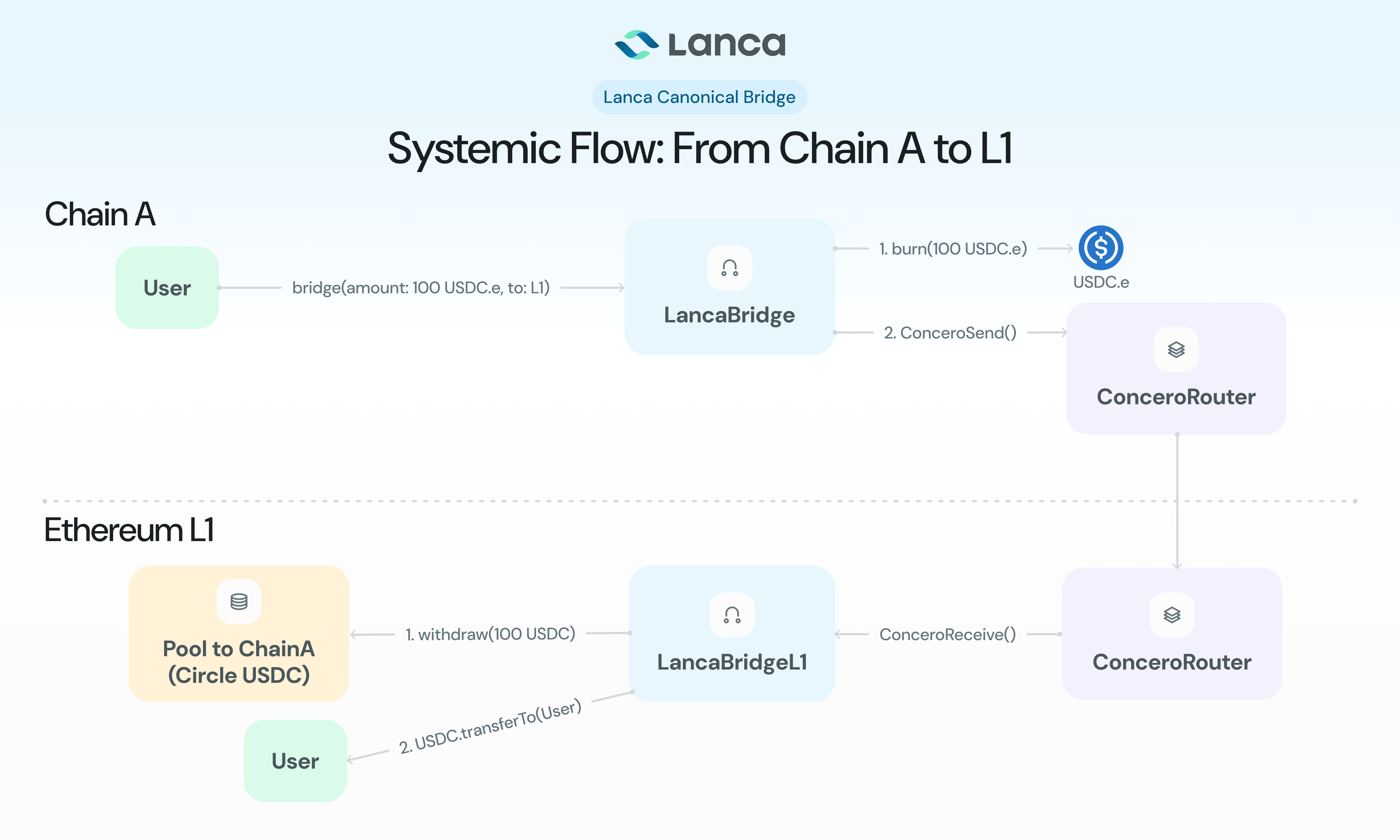
Systemic Flow: From Chain A to L1
System Components
LancaCanonicalBridgeL1
The main contract deployed on Ethereum (L1) that orchestrates the entire bridging process. It serves as the central hub that manages relationships with destination chains, coordinates token deposits into chain-specific pools, and handles cross-chain message routing via Concero Router.
When users initiate transfers, the L1 bridge accepts USDC deposits, routes tokens to the appropriate destination-specific pool, and sends cross-chain messages to destination chains. For return transfers, it receives burn notifications from destination chains and withdraws corresponding amounts from pools to complete the bridging cycle. The L1 bridge also handles smart contract integration through the callback mechanism, executing contract calls when recipients implement the client interface.
LancaCanonicalBridgePool
Individual pool contracts deployed on L1, each dedicated to a specific destination chain. These pools implement the Lock-Release mechanism by holding USDC collateral that backs bridged tokens on their respective destination chains.
Each pool operates in isolation, providing transparent proof of reserves for its destination chain. This architecture offers clear fund allocation, simplified migration paths for Circle's native USDC expansion, and isolated risk management per chain. The pools handle deposit and withdrawal operations exclusively through the L1 bridge contract, ensuring controlled access to locked collateral.
LancaCanonicalBridge
Destination chain contracts that implement the Burn-Mint mechanism for USDC.e tokens. Each destination chain has its own bridge contract that communicates directly with the L1 bridge to maintain the canonical bridging flow.
These contracts receive cross-chain messages from L1 and mint USDC.e tokens for incoming transfers. For outgoing transfers, they burn user tokens and send notifications back to L1. The destination bridges also handle smart contract integration through the callback mechanism, executing contract calls when recipients implement the client interface.
Cross-Chain Message Flow
L1 → Destination Transfer
- User Deposit: User calls
sendToken()on LancaCanonicalBridgeL1 - Pool Deposit: Bridge contract deposits USDC to destination-specific pool
- Message Creation: Bridge encodes transfer details and recipient information
- Cross-Chain Relay: Concero Router relays message to destination chain
- Token Minting: Destination bridge mints USDC.e to recipient
- Contract Callback: If recipient is a contract, execute
lancaCanonicalBridgeReceive()
Destination → L1 Transfer
- Token Burning: User calls
sendToken()on destination LancaCanonicalBridge - USDC.e Burn: Bridge burns user's USDC.e tokens
- Message Creation: Bridge encodes burn details and recipient information
- Cross-Chain Relay: Concero Router relays message to L1
- Pool Withdrawal: L1 bridge withdraws USDC from appropriate pool
- Token Transfer: L1 bridge transfers USDC to recipient
- Contract Callback: If recipient is a contract, execute
lancaCanonicalBridgeReceive()
Security Architecture
Rate Limiting System
Each bridge contract implements configurable rate limiting to prevent excessive token flow and provide time for emergency response.
Rate Limiting Parameters:maxAmount: Maximum tokens that can be bridged in the time windowrefillSpeed: Rate at which the limit refills over timeisOutbound: Separate limits for outbound vs inbound transfers
Contract Integration Support
Client Interface
Smart contracts can receive bridged tokens through the ILancaCanonicalBridgeClient interface:
interface ILancaCanonicalBridgeClient {
function lancaCanonicalBridgeReceive(
address token,
address sender,
uint256 amount,
bytes calldata data
) external returns (bytes4);
}Magic Value Validation
Contracts must return the correct magic value to confirm successful processing:
require(
expectedSelector == ILancaCanonicalBridgeClient.lancaCanonicalBridgeReceive.selector,
ILancaCanonicalBridgeClient.CallFiled()
);